API
Layers has a REST API from which it is possible to access the data stored in the system as well as updating customer, and fields information.
Check the available resources in PROD environment here.
Check the available resources in DEV environment here.
1. API end points
Users
Method |
Call |
Description |
|---|---|---|
POST |
/publicapi/customer |
Create customer request. Response will return the basic parameters of customer(farmer) to set other entites like fields or seasons. |
PUT |
/publicapi/customers/{customer} |
Update customer name. |
GET |
/publicapi/customers |
Get all customers. Provides a list of all user’s customers. |
GET |
/publicapi/cooperatives |
Get all cooperatives. Provides a list of all user’s cooperatives. |
POST |
/publicapi/getApiKey |
Get API key. Given an user/customer username and password provides an API key. |
GET |
/publicapi/user |
Get user profile information. |
Fields
Method |
Call |
Description |
|---|---|---|
GET |
/publicapi/fieldTypes |
Get all field types and subtypes. Provides a list of all the types (crops) available and sub_types (sub_crop). If a different crop is required contact via support@hemav.com |
GET |
/publicapi/irrigationType |
Get all irrigation types. Provides a list available. If a different irrigation is required contact via support@hemav.com |
GET |
/publicapi/fields |
Get all fields. Provides a list of all user’s fields. |
POST |
/publicapi/field |
Create new field. Requires at, least a customer_id and a name. |
PATCH |
/publicapi/field/{field} |
Edit a field. Given a field_id, modifies the passed parameters (i.e. name, external_reference_id, customer_id). |
Seasons
Method |
Call |
Description |
|---|---|---|
GET |
/publicapi/seasonParameters |
Get season available parameters. Provides a list of all season parameters and its units. |
GET |
/publicapi/seasonLogTypes |
Get available season log types. |
GET |
/publicapi/seasons/{season}/seasonLogs |
Get logs by season. |
GET |
/publicapi/seasons/{season}/snapshots |
Get snapshots by season. |
GET |
/publicapi/seasons/{season}/parameters |
Get a single season parameter. Given a season, return its parameters. |
POST |
/publicapi/seasons/{season}/parameters/{parameter} |
Post a single season parameter value. Given a season and a parameter, creates it with a value. |
PATCH |
/publicapi/seasons/{season}/parameters/{parameter} |
Patch a single season parameter value. Given a season and a parameter, edits its value. |
DELETE |
/publicapi/seasons/{season}/parameters/{parameter} |
Delete a single season parameter value. Given a season and a parameter, deletes it. |
GET |
/publicapi/fields/{field}/seasons |
Get all field associated seasons. Given a field, returns all its seasons. |
POST |
/publicapi/fields/{field}/season |
Create new season. Given a field, creates a new season, requires startDate and endDate. |
PATCH |
/publicapi/seasons/{season} |
Update field season. Given a season, updates its values. |
Snapshots
Method |
Call |
Description |
|---|---|---|
GET |
/publicapi/snapshots/sources |
Get snapshots available sources. |
GET |
/publicapi/seasons/{season}/snapshots |
Get snapshots and delivery metadata by season. |
Reports
Method |
Call |
Description |
|---|---|---|
GET |
/publicapi/reportTypes |
Get available report types. |
GET |
/publicapi/reportStatuses |
Get report statuses. |
GET |
/publicapi/reports |
Get user reports by date range. |
Postman collection
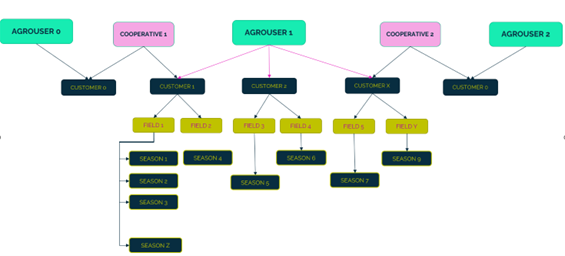
2. HEMAV DB Organization
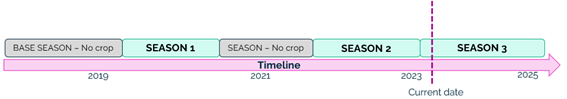
3. Workflows
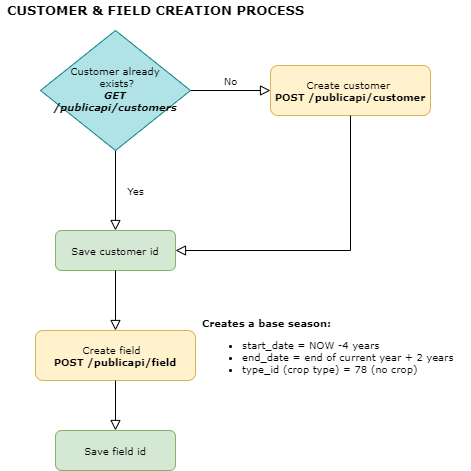
3.1. Customer & field creation
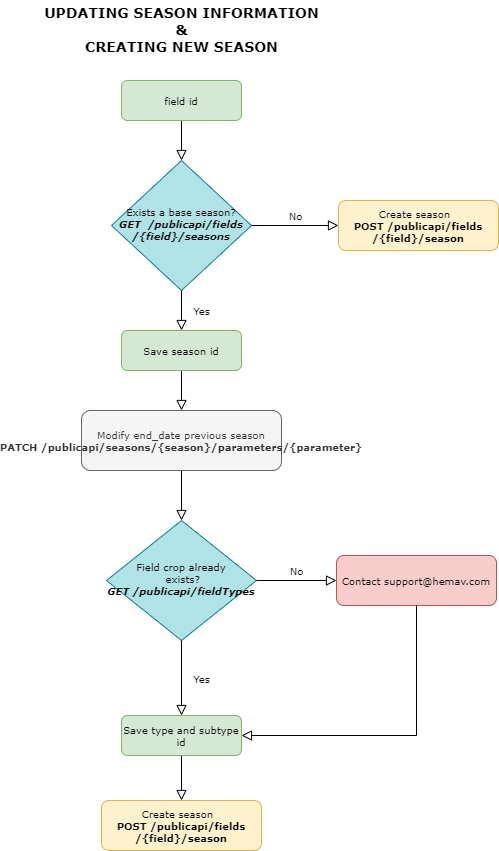
3.2. Update season information and creating new season
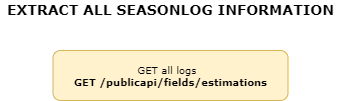
3.3. Extracting HEMAV DB information
3.3.1. Sat-tech, Planet, Landsat9 and drone-tech. Snapshot sources.

3.3.2. Weather, Irrigation and Pred-tech. SeasonLog types.

4. Season requirements and limitations
4.1. Fields
All fields must be unique in our DB. For this reason, besides our internal field identification (field_id) it is highly recommended that external_reference_id is used to create a unique value in our DB. Some recommendations to create this parameter are:
‘external_reference_id’ = ‘customer_id’ + ‘_’ + ‘field_id’
‘external_reference_id’ = ‘customer_id’ + ‘_’ + ‘name’
‘external_reference_id’ = ‘customer_id’ + ‘_’ + ‘id’
4.2. Seasons
There must always be a season opened in the current date.
Base season is opened when a field is created with start_date -4 years and end_date is set to end of current year + 2 years.
Type_id (crop) is set to 78 (no crop)
Time gaps between seasons are not allowed. Start_date new season must be end_date previous season + 1 day. For this purpose, no crop seasons are created by our system if seasons are not consecutive.
It is important to use the same season label located in the same area with the same start_date and end_date. This will help in Layers visualization but also in data processing.
Season format:
{
"startDate": "2023-01-01",
"endDate": "2025-12-31",
"geometry": "string",
"surface": 0,
"type": 0,
"subType": 0,
"irrigationType": 0,
"label": "string",
"parameterValues": [
{
"value": "string",
"extraInfo": "string",
"season": 0,
"parameter": 0
}
]
}Mandatory keys for season creation are: startDate, endDate, type and label. Nevertheless, it is highly recommended to include as many as possible as they will help if any predictive product is contracted.
How do we set a desired season situation for a field?
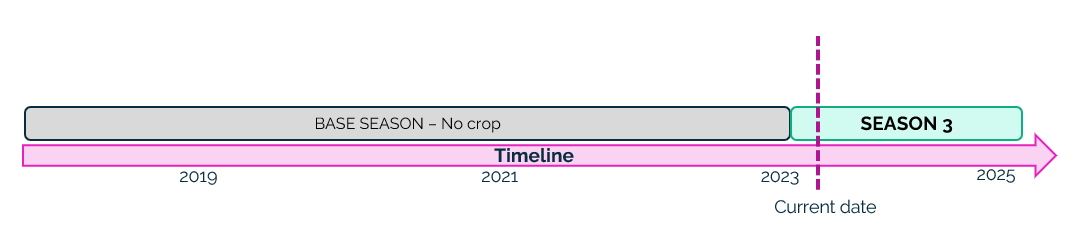
Step 1 – Last season is processed first, as its start_date is greater than the start_date of the Base season – No crop. Base season no crop is closed with end_date equal to start_date of season 3 – 1 day.
Season 3 is created with its start and end date (which should be a future date).
Now we have the following situation:
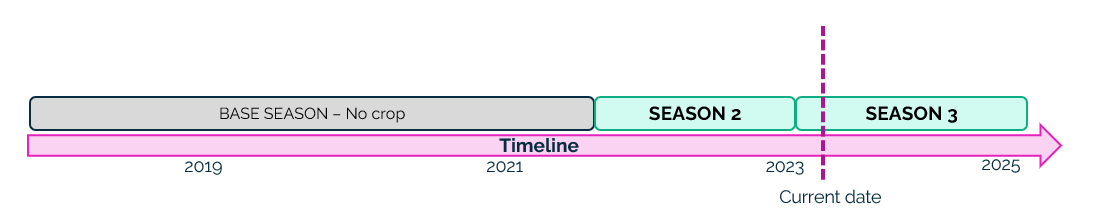
Step 2 – Now we process Season 2. As its start_date is greater than the start_date of the BASE No crop season, season no crop is closed with end_date equal to start_date of season 2 – 1 day.
On the other hand, as its end_date is equal to start_date of season 3 – 1 day, we do not need a NO CROP season between season 3 and season 2.
Season 2 is created with its start and end date.
Now we have the following situation:
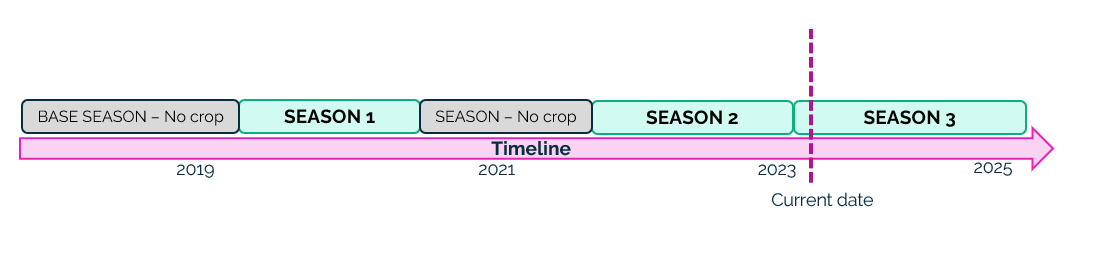
Step 3 - Season 3 is processed, as its start_date is greater than the start_date of the BASE No crop season, season no crop is closed with end_date equal to start_date of season 1 – 1 day.
If end_date of season 1 is smaller by more than one day than start_date of season 2, a no crop season is needed.
For this reason, season 1 with its start and end date is created. But also a new NO CROP season needs to be created which will have start_date equal to end_date of season 1 + 1 day and end_date equals to start_date of season 2 – 1 day.
Thus, we obtain the desired situation:
4.3. Geometries
Geometries must be coordinates, in degrees, in WGS84 CRS. It is the only format accepted.
Geometry example:
{
"geometry": "[[[[37.048924745685, -7.7634227285916], [37.049831149291, -7.7634268877869], [37.04982697993, -7.7643309260375],
[37.048920574389, -7.7643267663521], [37.048924745685, -7.7634227285916]]]]"
}4.4. Season parameters
| id | name | measure_unit short_name | measure_unit lond_name | SAT TECH | SAT PRED | SOIL TECH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | production | kg/ha | Kilograms/Hectar | |||
| 2 | plantation_date | Soy, beetroot, corn | ||||
| 3 | pattern | m | Meters | |||
| 4 | plantation_frame | |||||
| 5 | plant_distance | |||||
| 6 | street_distance | |||||
| 7 | random_seedling | |||||
| 8 | random_fertilization | |||||
| 9 | auto_harvest | |||||
| 10 | irrigation_emitters | |||||
| 11 | irrigation_limit | m3 | Meters3 | |||
| 12 | irrigation_level | m3 | Meters3 | |||
| 13 | vulnerability | |||||
| 14 | cut_number | Sugar cane | ||||
| 15 | estimated_harvest_date | Sugar cane | ||||
| 16 | harvest_date | Sugar cane | ||||
| 17 | agoste_date | |||||
| 18 | backfertilization_estimated_date | |||||
| 19 | backfertilization_estimated_dose | kg/ha | Kilograms/Hectar | |||
| 20 | backfertilization_estimated_N | |||||
| 21 | backfertilization_estimated_P | |||||
| 22 | backfertilization_estimated_K | |||||
| 23 | backfertilization_date | |||||
| 24 | backfertilization_dose | kg/ha | Kilograms/Hectar | |||
| 25 | backfertilization_N | |||||
| 26 | backfertilization_P | |||||
| 27 | backfertilization_K | |||||
| 28 | coverfertilization_estimated_date | |||||
| 29 | coverfertilization_estimated_dose | kg/ha | Kilograms/Hectar | |||
| 30 | coverfertilization_estimated_N | |||||
| 31 | coverfertilization_estimated_P | |||||
| 32 | coverfertilization_estimated_K | |||||
| 33 | coverfertilization_date | |||||
| 34 | coverfertilization_dose | kg/ha | Kilograms/Hectar | |||
| 35 | coverfertilization_N | |||||
| 36 | coverfertilization_P | |||||
| 37 | coverfertilization_K | |||||
| 40 | irrigation_estimated_date | |||||
| 41 | irrigation_date | |||||
| 42 | ATR_target | |||||
| 43 | ATR_real | ATR model | ||||
| 44 | ATR_per_hectare_target | |||||
| 45 | ATR_per_hectare_real | tn/ha | Tones/Hectar | |||
| 46 | maturing_estimated_date | |||||
| 47 | maturing_estimated_dose | |||||
| 48 | maturing_estimated_product | |||||
| 49 | maturing_date | |||||
| 50 | maturing_dose | |||||
| 51 | maturing_product | |||||
| 52 | phytosanitary_date | |||||
| 53 | phytosanitary_dose | |||||
| 54 | phytosanitary_estimated_date | |||||
| 55 | phytosanitary_estimated_dose | |||||
| 56 | phytosanitary_estimated_product | |||||
| 57 | phytosanitary_product | |||||
| 58 | SAC_real | SAC model | ||||
| 59 | type_of_soil | |||||
| 60 | harvest_surface | ha | Hectar | |||
| 61 | ATR_estimate | |||||
| 62 | production_per_hectare_estimate | tn/ha | Tones/Hectar | |||
| 63 | POL_target | |||||
| 64 | POL_real | POL_model | ||||
| 66 | customer_sub_type | |||||
| 67 | irrigation_turn | |||||
| 69 | irrigation_type | |||||
| 70 | previous_crop | |||||
| 71 | SAC_target | |||||
| 72 | POL_estimate | |||||
| 73 | SAC_estimate | |||||
| 74 | production_target | tn/ha | Tones/Hectar | |||
| 75 | production_real | tn/ha | Tones/Hectar | |||
| 76 | production_estimate | tn/ha | Tones/Hectar | |||
| 77 | plants_per_hectare | |||||
| 78 | n_bunches_real | unit/ha | unit/ha | Bunches model |
| Mandatory | Desirable | Recommended |
5. Step by step - Creating and updating season information
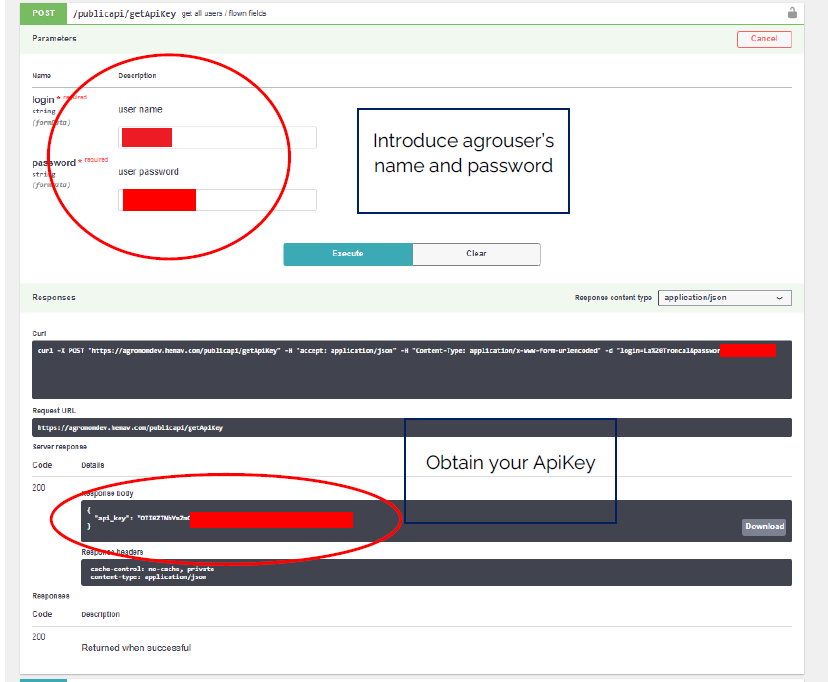
5.1. Get ApiKey
First of all, get your user’s api key.
5.3. Get information of all your customers
Obtain your customer’s information.
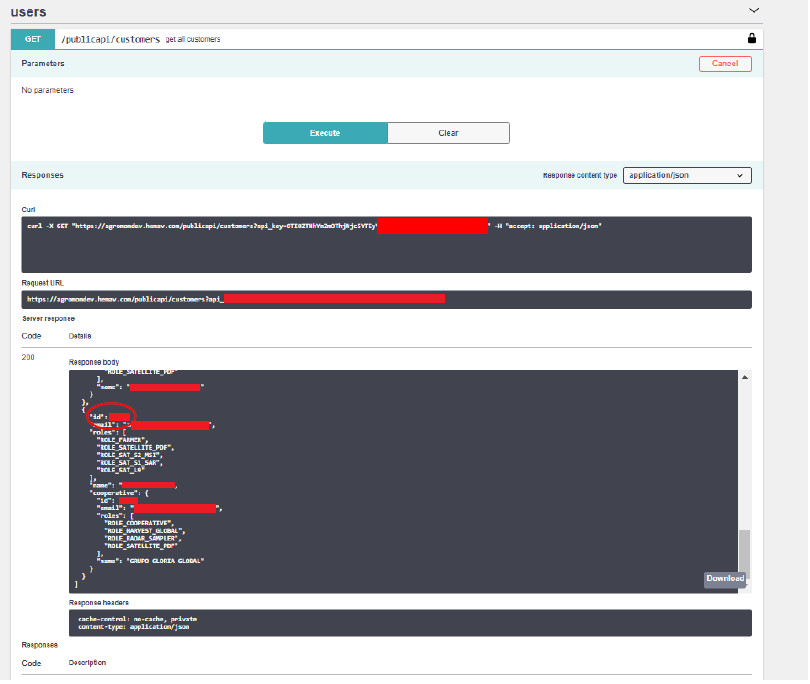
From the obtained data, we need to keep the customer’s id from the customer that we need to create a field.
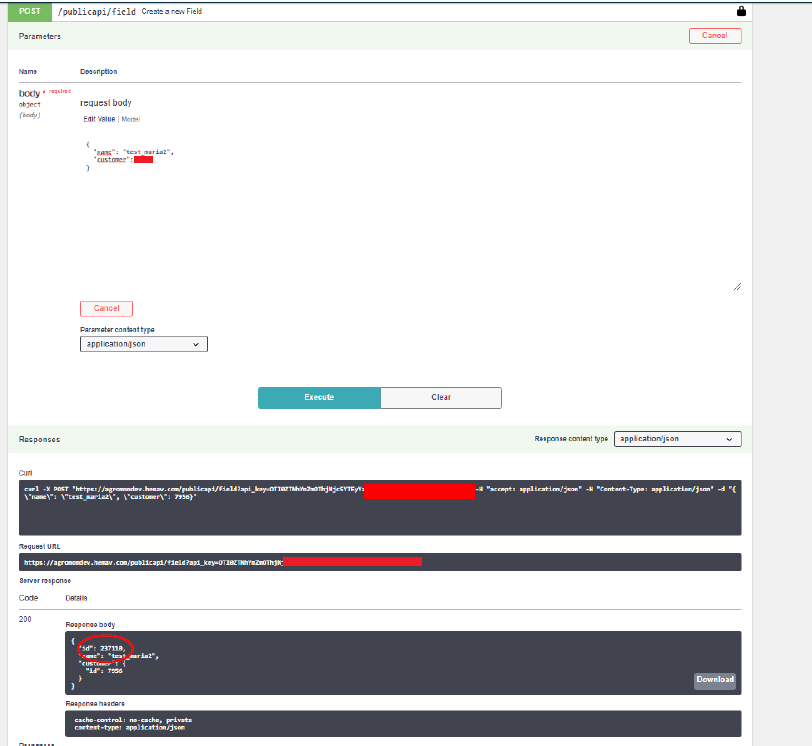
5.4. Create a field
Using the customer id obtained from the previous step, we create a new field. We keep this field_id.
5.5. Check field season information
As we can check in our DB, the field creation, also creates a BASE SEASON with type_id = 78 (no crop) with start_date set as minus four years from the creation date and end_date is set as the end of the current year plus two.
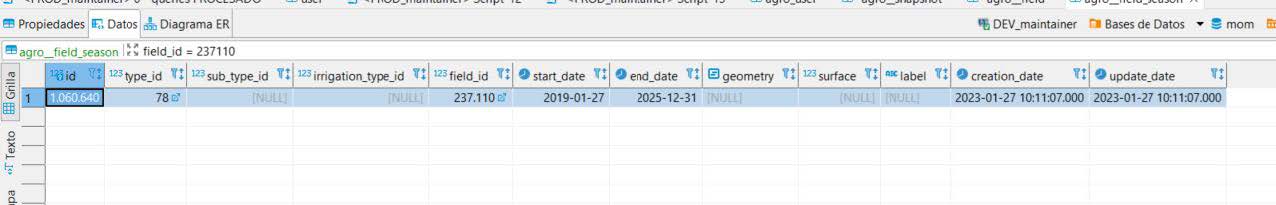
This information can also be checked from the API.
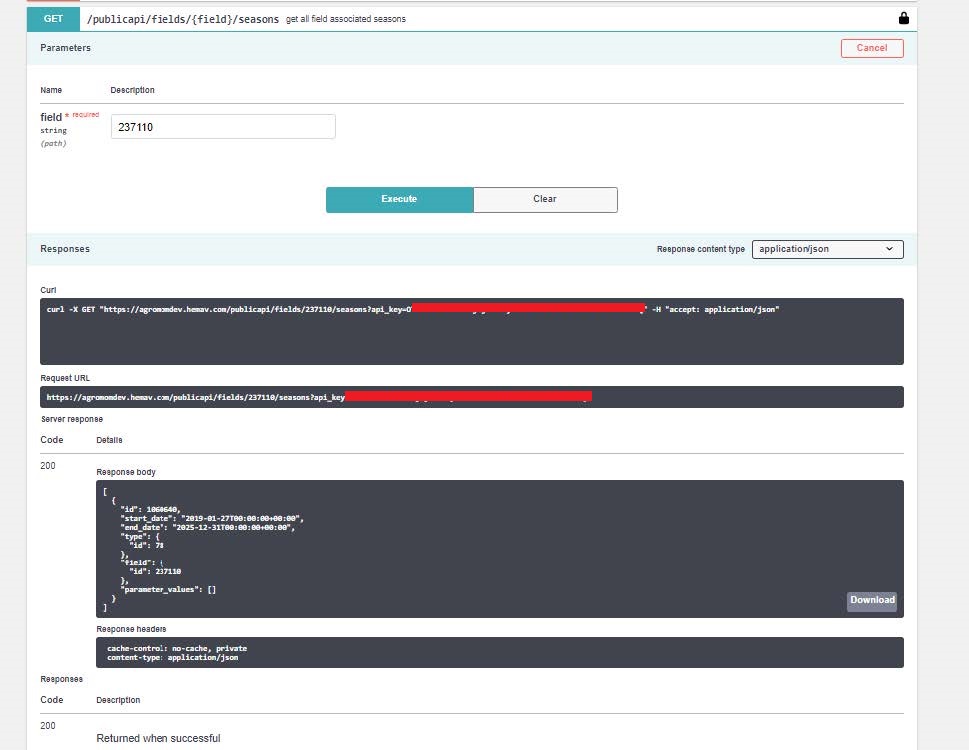
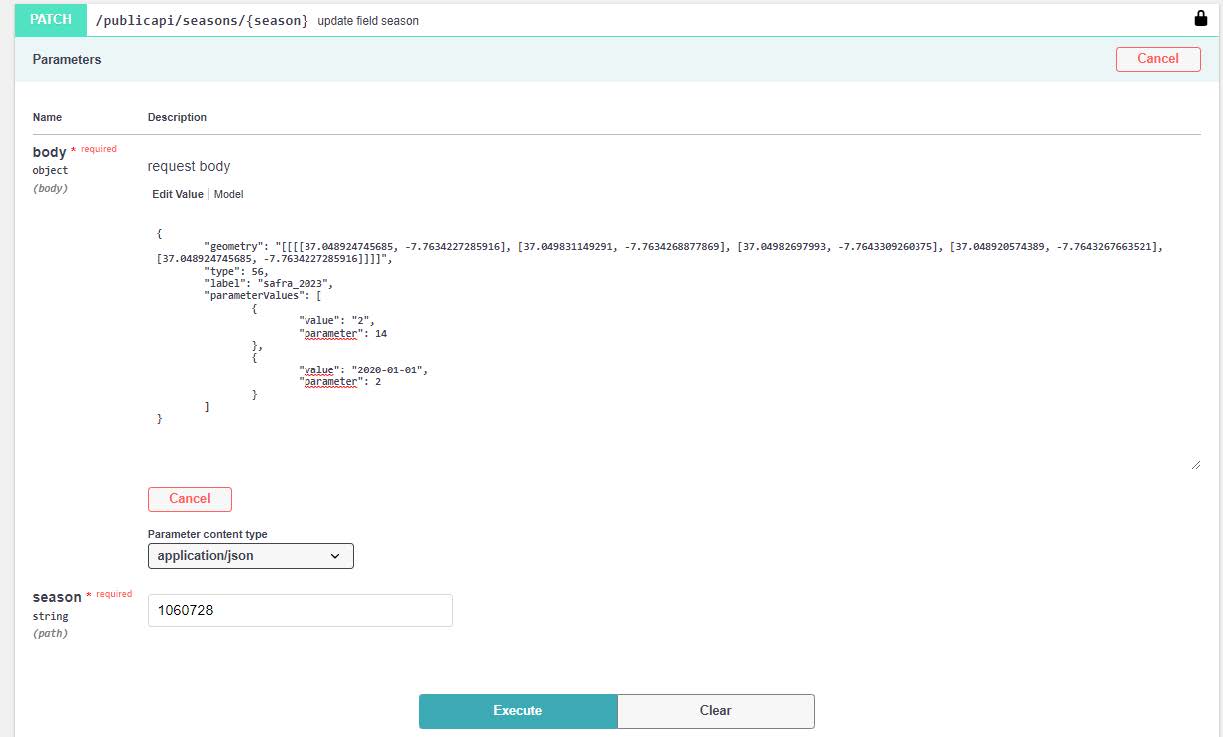
5.6. Update season
Whether we have a recently created field, which have a base season without information, or we want to update the season’s information of a field, the PATCH method /publicapi/seasons/{season} will be used.
Only parameters that need to be modified should be included.
{
"geometry": "[[[[37.048924745685, -7.7634227285916], [37.049831149291, -7.7634268877869], [37.04982697993, -7.7643309260375], [37.048920574389, -7.7643267663521], [37.048924745685, -7.7634227285916]]]]",
"type": 56,
"label": "safra_2023",
"parameterValues": [
{
"value": "2",
"parameter": 14
},
{
"value": "2020-01-01",
"parameter": 2
}
]
}In this example we will update the geometry, the crop (type 56 corresponds to sugar cane) and the season parameters 14 and 2, which corresponds to cut number and plantation date.
Depending on the crop and the contracted products different parameters will be required. You can find more information regarding season parameters on section 4.4 of this documentation.
6. Extracting information
6.1. Sat-tech, Planet, Landsat9 and drone-tech. Snapshot sources.
source_id |
Description |
Exracted Parameters |
|---|---|---|
1 |
Drone with multispectral camera |
Depending on the contracted deliveries. lines_l, overs_l, ndre_std, ndvi_std, nrel_std, overs_pl, ndre_mean, ndvi_mean, nrel_mean, sector_id, alert_perc, overs_stats, overs_mean_length, sector_area, plants_count, weeds_perc_fe, weeds_perc_fl, resowing_count, nitrogen_relative_std, nitrogen_relative_mean. |
3 |
Satellite Sentinel 2 |
Cloud coverage, kc, ndre_mad, ndre_max, ndre_min, ndre_std, ndvi_mad, ndvi_max, ndvi_min, ndvi_std, ndre_mean, ndvi_mean, sector_id, ndre_median, ndvi_median, sector_area, moisture_mad, moisture_max, moisture_min, moisture_std, moisture_mean, ndre_kurtosis, ndvi_kurtosis, moisture_median, scene_product_id, moisture_kurtosis, ndre_first_quartile, ndre_third_quartile, ndvi_first_quartile, ndvi_third_quartile, scene_classification, nitrogen_relative_mean, moisture_first_quartile, moisture_third_quartile, potassium_relative_mean, ndre_interquartile_range, ndre_outliers_percentage, ndvi_interquartile_range, ndvi_outliers_percentage, phosphorus_relative_mean, moisture_interquartile_range, moisture_outliers_percentage. |
6 |
Drone with RGB camera |
Depending on the contracted deliveries, usually weeds and failures data. |
8 |
Satellite Sentinel 1 SAR ascending orbit |
Cloud_coverage, sector_id, std_sigma0, mean_sigma0, sector_area, scene_product_id. |
9 |
Satellite Sentinel 1 SAR descending orbit |
Cloud_coverage, sector_id, std_sigma0, mean_sigma0, sector_area, scene_product_id. |
10 |
Satellite Planet |
Bands, ndre, ndvi, sector_id, quality_bands. |
11 |
Satellite Landsat 9 |
Cloud_coverage, bands, ndmi, ndvi, termal, sector_id, quality_bands, name cloud, scene_product_id |
6.2. SeasonLog types. Weather, Irrigation and Pred-tech.
type_id |
Name |
|---|---|
1 |
SAC_ha |
2 |
PROD_ha |
10 |
WEATHER_historic |
11 |
WEATHER_forecast |
12 |
WEATHER_alert |
15 |
TCH_pred |
16 |
ATR_pred |
17 |
NITRO |
21 |
IRR_needs_forecast |
22 |
IRR_needs_historic |
23 |
POL_pred |
24 |
n_bunches_pred |